Microscope objectives
An introduction to 'infinity' corrected microscope objectives.
ContentsPlan correction
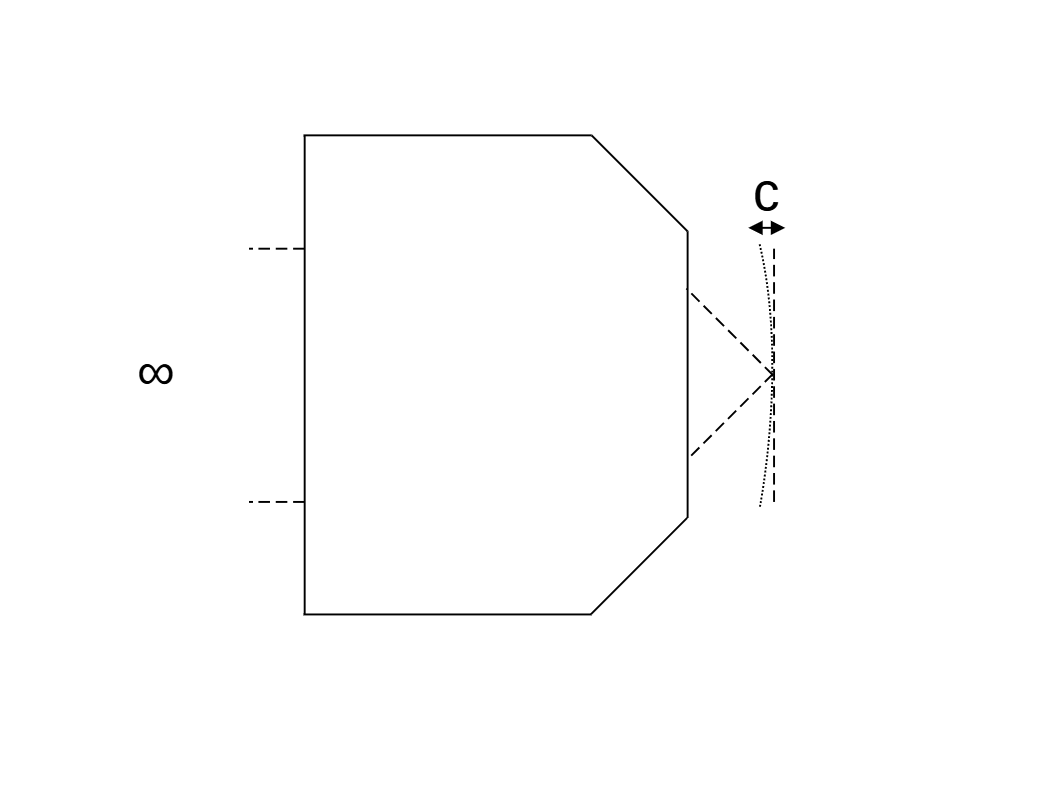
An ideal objective would image a totally flat plane and be fully 'plan' corrected. In practice the lens design has to battle field curvature, which naturally occurs when a series of (mostly positive) elements are combined to make an objective (Hecht 2016). From Zhang 2019, an objective can be considered 'plan' corrected if, the difference \(C\) between the best focus at the field edge and the best axial focus, is less than 2.5x the traditional depth of field: \[ C \leq 2.5 \frac{n\lambda}{NA^2} \tag{1}\] So for sensitive applications this could be considered quite a loose tolerance, and therefore, the field curvature on a non-plan objective may be quite pronounced.